In January 2006, Malaysian Accounting Standards Board (MASB) issued Exposure Draft ED 50 Agriculture for public comments by professional accounting bodies, regulators, users and other interested parties. The ED 50 was closed for comments by March 2006, and remains outstanding and pending further review or pending conclusion by MASB. As of May 2011, even after so many years since the exposure draft issued, ED 50 Agriculture has not been adopted as final Financial Reporting Standard (FRS) in Malaysia.
ED 50 is identical with IAS 41 Agriculture that was issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) on 22 February 2001.
On 1 August 2008, the FRF and MASB announced their plan to bring Malaysia to full convergence with IFRS by 1 January 2012. If the convergence deadline is still on and not delay, 1 January 2012 would be the effective date in Malaysia for applying IAS 41.
Malaysia is the world’s second largest producer and exporter of palm oil. As such, the adoption of IAS 41 will definitely have a great impact to many palm oil plantation companies in Malaysia. To name a few listed companies, like Sime Darby, Kuala Lumpur Kepong (KLK), IOI Corporation, Kulim Malaysia and Tradewind Plantation. Unlisted companies like Felda and Felcra.
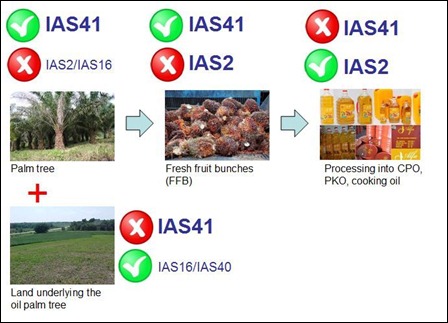
Application of IAS 41 and IAS 2 in oil palm plantation and palm oil processing:
Biological asset (eg. oil palm tree)
A biological asset is a living animal or plant/tree. Biological assets should be measured on initial recognition and at subsequent reporting dates at fair value less estimated costs to sell (separately from the land), unless fair value cannot be reliably measured.
The land underlying the biological asset is accounted for as an asset in accordance IAS 16 or IAS40. IAS 41 does not deal with land underlying the biological asset.
Agricultural produce (eg. fresh fruit bunches – FFB)
Agricultural produce is the harvested product of the entity’s biological assets. Agricultural produce should be measured at fair value less estimated costs to sell at the point of harvest.
Processed oil products (eg. CPO, PKO, Cooking oil)
Thereafter the point of harvest, IAS 2 Inventories is applied. IAS 42 does not deal with the processing of agricultural produce after harvest.
What is fair value less estimated costs to sell ?
Fair value generally refers to market value. Costs to sell include commissions to brokers and dealers, levies by regulatory agencies and commodity exchanges, and transfer taxes and duties. Costs to sell exclude transport and other costs necessary to get assets to a market.
See related post: MASB calls for IAS 41 post-implementation review